Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are autonomous systems that leverage various tools and models to achieve specified objectives. They maintain memory across tasks and evolving contexts, utilize one or more AI models to carry out operations, and autonomously determine when to interact with internal databases or external services on behalf of a user. As a result, these agents can make informed decisions and execute actions with minimal human intervention.
Example of day-to-day business use case: A global consumer goods firm wanted to enhance its marketing efficiency. By deploying an AI agent, a workflow previously demanding six analysts over a week now requires only one person plus the agent, producing actionable insights in under an hour. The process unfolds as follows.
- The AI agency provides Data Aggregation. The agent autonomously extracts and consolidates marketing data weekly through integrated pipelines.
- The AI agent performs a Performance Analysis by evaluating campaign metrics in context, comparing actual outcomes against targets, and consulting an operator when additional business context is needed.
- The AI agent provides a series of recommendations. The agent drafts a standardised report with optimisation proposals; an operator then rigorously tests and fine-tunes these suggestions.
- The AI agent executes Updates. Upon human approval, the agent implements the recommended changes across media buying platforms.
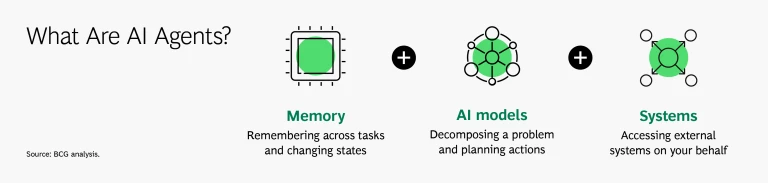
How Do AI Agents Work?
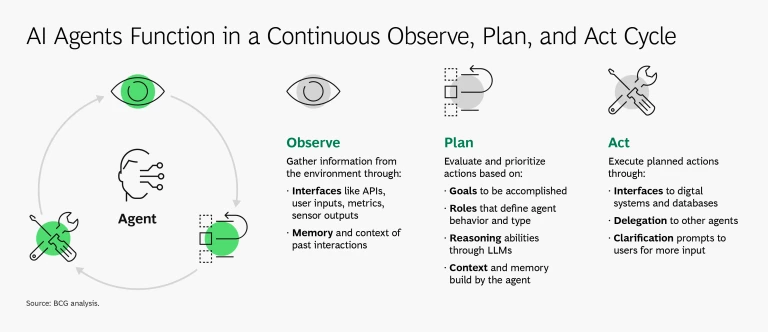
AI agents observe their environment, leverage large language models for Observe → Plan → Act within the business environment.
- Observe: AI agents continuously ingest real-time inputs—ranging from user interactions and key performance indicators to sensor outputs—and retain both short-term and long-term contextual memory for multi-step operations.
- Plan: Utilizing large language models (LLMs), agents autonomously prioritize and sequence actions based on objectives, environmental context, and accumulated memory.
- Act: Through API integrations with enterprise systems (e.g., HR platforms, CRM tools, order management), agents execute tasks defined by their plan. They can also hand off subtasks to other agents or solicit clarifications when required. Internal checks allow them to detect and correct errors, refining their approach over successive iterations.
This continuous observe-plan-act loop enables agents to learn from past interactions, adapt to environmental changes, and optimize their performance over time.
What Are the Components of an AI Agent?
AI agents vary in implementation but tend to have five components:
- Interface Layer
Connects the agent to users, databases, sensors, and external services via APIs and protocols. - Memory Store
Consists of short-term memory for current tasks and long-term memory for factual knowledge, conversation histories, and previous task details. - Profile Module
Defines the agent’s role, objectives, and behavioral guidelines. - Planning Engine
Typically powered by an LLM or small language model (SLM), this module synthesizes observations, memory, and profile data to formulate actionable plans. - Action Module
Houses the APIs and system integrations that enable the agent to perform its designated functions.
What Do AI Agents Do?
AI agents represent a new era in artificial intelligence, far surpassing traditional software. Unlike static tools, these intelligent software agents act as autonomous, decision-making entities. They analyze data, plan tasks, take action, and continuously adapt—often in real time. Here’s what makes them so powerful:
- Initiative & Adaptability
- Rather than passively awaiting instructions, AI agents proactively engage with their surroundings, updating plans in real time as conditions shift, unlike rigid robotic process automation.
- System Integration & Collaboration
- They execute tasks by interfacing with enterprise systems and can coordinate with other agents to complete complex workloads.
- Continuous Improvement
- With built-in feedback loops and error-correction routines, agents refine their strategies and enhance efficiency across repeated cycles.
What Are the Types of AI Agents?
AI agents vary in complexity, from simple coding assistants to complex networks that can automate processes that require teams of people today. Using coding as an example, we can see the different levels of sophistication that can be achieved with various types of intelligent agents:
- Basic Coding Copilot generates code snippets in response to developer prompts.
- Context-Aware Agent Ingests an existing codebase and tailors its outputs, even autonomously writing code that satisfies unit tests once tests are defined.
- Full-Lifecycle Dev Agent. Beyond coding, this agent compiles and tests applications in staging environments.
- Deployment-Capable Agent Upon human approval, future iterations may automatically deploy tested applications through CI/CD pipelines, enabling end-to-end development via conversational instructions.
How Do You Use AI Agents?
AI agents excel when tasks can be decomposed into clear, bounded subtasks and receive relevant context alongside rapid feedback. Three primary value streams emerge:
- Process Automation
Efficiently handle repetitive workflows, freeing employees for strategic work. - Human–Agent Collaboration
Act as intelligent teammates, supplying insights, supporting decisions, and executing tasks that augment human expertise. - Data Insight Generation
Analyze vast datasets to uncover patterns and strategic insights beyond human scale.
How Are Businesses Using AI Agents Today?
AI agents are fast becoming common across industries. Early adopters have already unlocked value from these intelligent software agents in multiple functions, including marketing and sales, customer service, R&D, and data and technology. But this is just the tip of the iceberg. Here are a few business cases for AI agents that companies are exploring today:
- Marketing: A leading consumer packaged goods company used intelligent agents to create blog posts, reducing costs by 95% and improving speed by 50x (publishing new blog posts in a single day instead of four weeks).
- Customer service: A leading global bank used AI virtual agents to interface with customers, reducing costs by 10x.
- Research and development: A biopharma company used AI agents for lead generation, reducing cycle time by 25% and gaining 35% in time efficiency for drafting clinical study reports.
- Data and technology: An IT department used AI agents to modernise its legacy technologies, increasing productivity by up to 40%.
Are AI Agents the Future?
AI agents are gaining traction quickly across various business applications, and the market for AI agents is expected to grow at a 45% CAGR over the next five years.
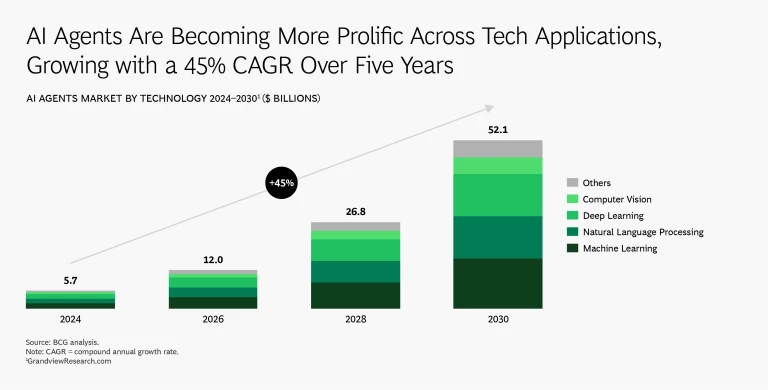
The AI agent market is projected to grow at approximately 45 % compound annual growth rate (CAGR) over the next five years. As these agents become ubiquitous, organizations will integrate them just like human hires—onboarding them with role definitions, system access, and workflow integration. Teams will shrink as agents take on more responsibilities, allowing companies to scale rapidly without proportionally increasing headcount.
Supervising AI agents will evolve into a critical skill, ensuring ethical standards, privacy, and fairness. As agent proliferation accelerates, businesses must invest in training employees at every level on responsible AI governance.
